The LICOMK++ developed under the leadership of CNIC, has been a finalist for the Gordon Bell Prize for Climate Modeling
Recently, the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) announced the list of research projects nominated for the 2024 ACM Gordon Bell Prize for Climate Modelling. Computer Network Information Center (CNIC) and Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, etc, were honored for their significant application "A Performance-Portable Kilometer-Scale Global Ocean Model on ORISE and New Sunway Heterogeneous Supercomputers" .
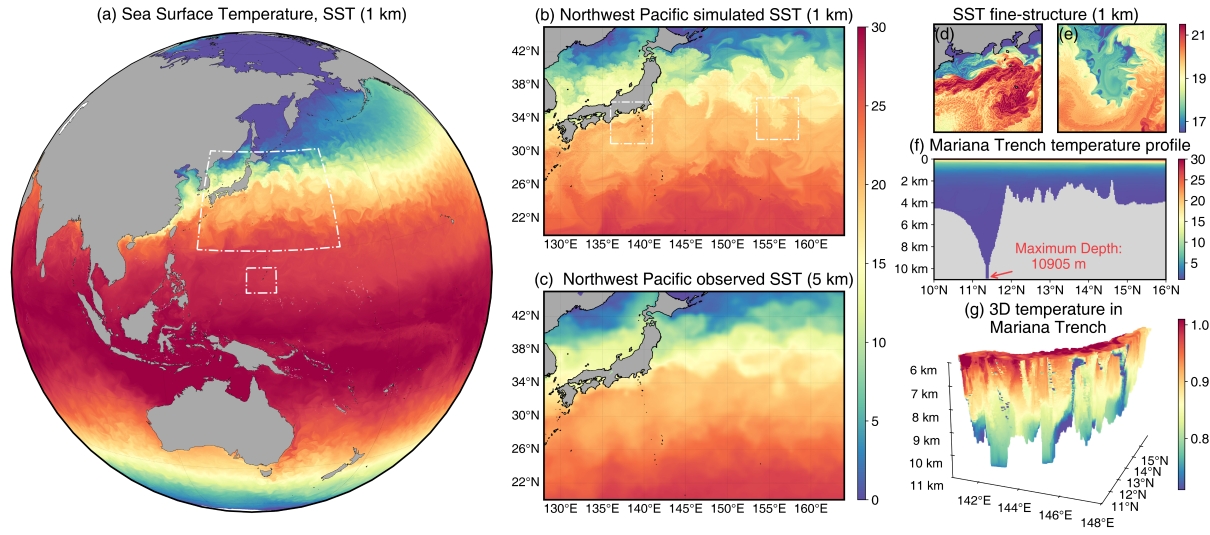
The research extended a performance-portable programming model to the new-generation Sunway supercomputing system, creating the world’s first global 1 km resolution, performance-portable oceanic general circulation model (LICOMK++). This model enabled the rapid deployment of a single codebase across mainstream supercomputing architectures, effectively harnessing the computational resources of various supercomputing systems to accelerate scientific simulations. LICOMK++ achieved remarkable scalability, utilizing up to 16,000 GPUs on the ORISE supercomputer and nearly 39 million cores on the new Sunway supercomputer. At a global 1-km resolution, the model surpassed the performance threshold of 1 simulated-years-per-day, successfully capturing mesoscale and sub-mesoscale oceanic structures and enhancing the scientific understanding of climate change. This breakthrough offers a solution to the challenge for programming faced by mainstream supercomputing systems worldwide. Additionally, it reduces uncertainties in oceanic general circulation model, providing scientific foundations and technical support for future climate change projections and extreme weather event predictions.