CNIC made progress in the research of cancer bioinformatics
Recently, researchers from the Department of High Performance Computing Technology and Application Development (HPC) have built upon previous studies to propose a deep learning-based multi-scale pathological image MSI prediction method, named MSIscope. This method is based on the Transformer architecture and is designed to address the multi-scale characteristics of pathological images and the specific pathological features of MSI. It incorporates modules for region of interest selection, multi-scale vision expansion, and multi-scale feature fusion, effectively locating and extracting features from key regions while integrating cross-region and cross-scale contextual information, thus overcoming the limitations of existing methods. Experiments show that the proposed method performs excellently on pan-cancer datasets, surpassing current similar methods with an AUROC of 0.911. Additionally, the model exhibits remarkable robustness even in pathological slides with low tumor purity. The proposal of MSIscope provides a new perspective for assessing MSI status and serves as an effective supplement to NGS-MSI detection algorithms such as MSIsensor.
This research has been accepted for presentation at the prestigious 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics & Biomedicine (BIBM, CCF B, regular paper). The co-first authors are PhD students Hu Taiyuan and Luan Haijing from HPC, with co-corresponding authors Prof. Niu Beifang and Dr. Li Ruilin. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Youth Project of the Basic Research Fund of the Computer Network Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
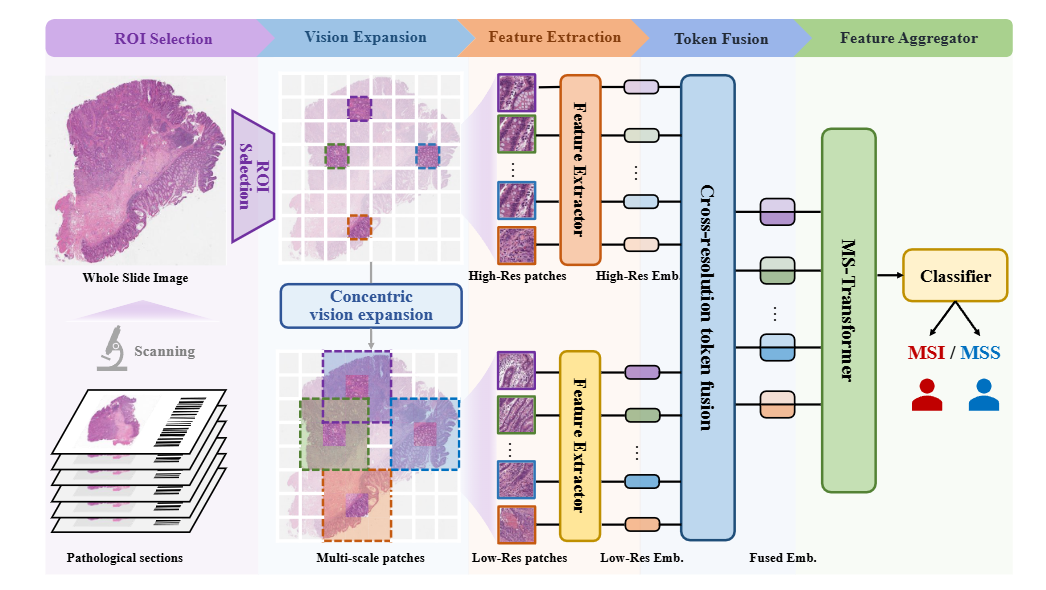
Overall architecture of MSIscope
