CNIC made progress in Large-Scale Flow-Field Visualization
Particle advection is a fundamental algorithm for flow-field visualization and analysis and is widely used in high-performance-computing (HPC) applications such as climate modeling, plasma physics, and engineering design. However, in in-situ visualization workflows that rely on the Parallelization-Over-Data (POD) strategy, the inherent imbalance of data partitions often causes load skew and communication congestion, creating performance bottlenecks.
The Advanced Interactive Technology and Application Development Department of our Center has carried out in-depth research on the issues outlined above. The team proposed a workload-estimation–driven strategy for scheduling multiple replicas of data blocks and developed a multi-stage data-scheduling algorithm based on workload prediction, reducing overall workflow execution time by roughly 30%. These results have been accepted for presentation at the Eurographics Conference on Visualization 2025 (CCF Class B conference). The research was supported by the National Key R&D Program. The paper’s first author is Associate Researcher Zhe Wang from our Center, and the co-corresponding author is Researcher Guihua Shan, also with our Center.
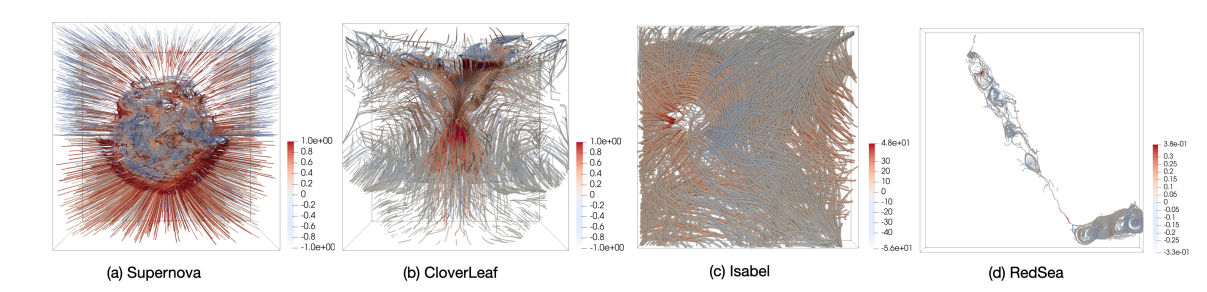
Figure 1. Visualization results of a load-imbalanced flow field.
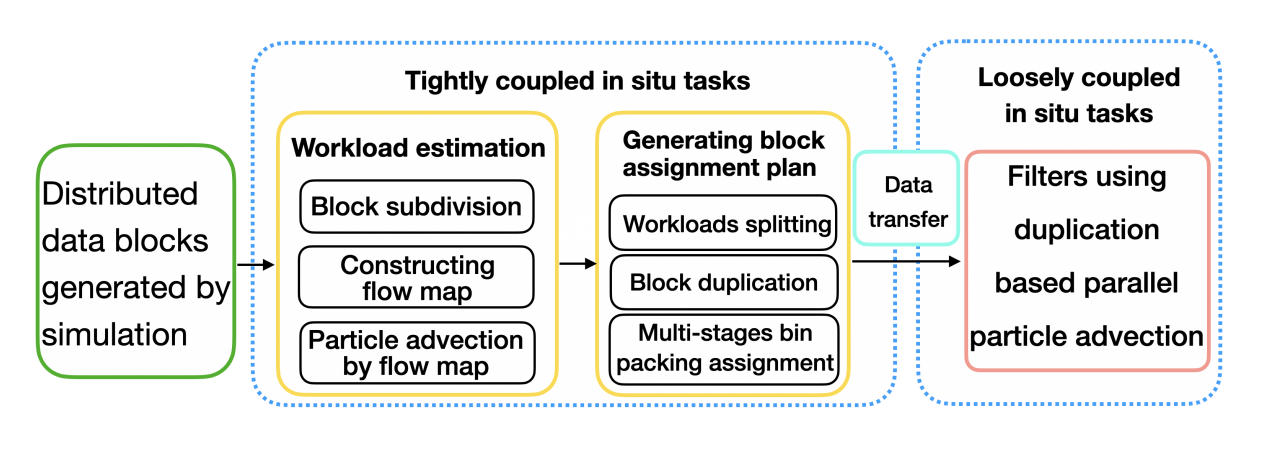
Figure 2. In-situ visualization workflow based on workload prediction and redistribution.
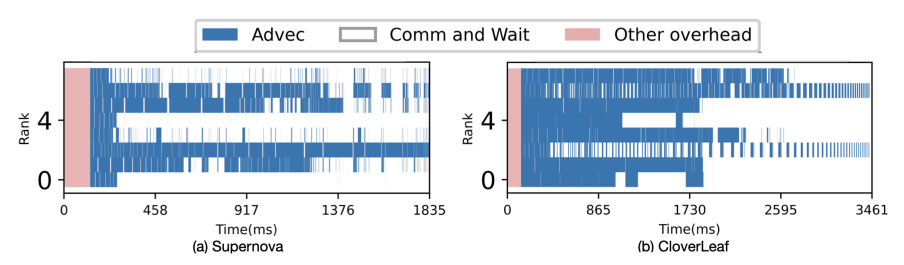
Figure 3. Data-block redistribution strategy reduces algorithm execution time through load balancing.
[1]Zhe Wang,Kenneth Moreland,Matthew Larsen,James Kress,Hank Childs,Guan Li,Guihua Shan,David Pugmire“In Situ Workload Estimation for Block Assignment and Duplication in Parallelization-Over-Data Particle Advection”,Eurographics Conference on Visualization 2025.
